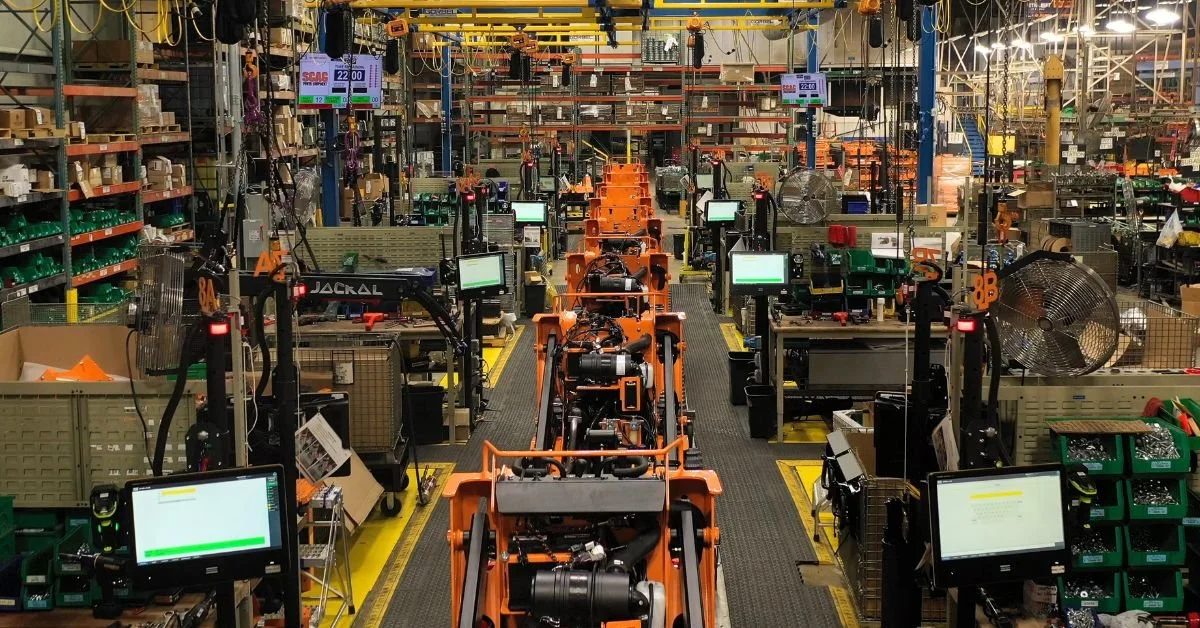
Industrial automation networks are reshaping how metalworking and machining operations connect, communicate, and coordinate their systems. These networks serve as the digital backbone that links programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), sensors, and robotic systems into unified production environments.
The evolution from isolated machines to interconnected smart factories represents one of the most transformative shifts in manufacturing history. Moreover, this transformation directly impacts your bottom line through improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced quality control.
Today’s automation networks go beyond simple device connectivity. They enable real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance capabilities, and centralized monitoring that puts you in complete control of your operations. Additionally, these networks provide the foundation for implementing Industry 4.0 principles that drive competitive advantage in modern manufacturing. Read on to take a deep dive into the current state and future of industrial automation networks, as well as learn how to leverage them for your operations.
Current State of Industrial Networking Technologies
Industrial Ethernet dominates the automation networking landscape, with protocols like EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, and Modbus TCP/IP leading the charge. These protocols deliver the speed and reliability your machining operations demand while maintaining compatibility with existing equipment.
Fieldbus systems continue to play crucial roles in many facilities, particularly those with legacy equipment investments. DeviceNet, PROFIBUS, and Foundation Fieldbus networks provide proven performance in harsh industrial environments where electromagnetic interference and temperature extremes challenge standard networking equipment.
Wireless Solutions Gaining Ground
Wireless industrial networks are making serious headway in metalworking facilities. WirelessHART and ISA100.11a protocols offer reliable communication for monitoring applications, while private 5G networks promise ultra-low latency connections for critical control functions.
The wireless industrial networking market is projected to see major growth by 2030 as manufacturers continue adopting wireless systems for critical operations.. This number reflects the many, many manufacturers implementing wireless solutions for mission-critical operations.
Emerging Technologies Reshaping Networks
Time-sensitive networking (TSN) represents a game-changing advancement for industrial communications. This IEEE standard enables deterministic data transmission over standard Ethernet infrastructure, eliminating the need for specialized industrial protocols in many applications.
TSN delivers precise timing synchronization that your CNC machines and robotic systems require for coordinated operations. Furthermore, it supports mixed traffic types on the same network, allowing operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) systems to coexist without interference.
Edge Computing Integration
Edge computing brings processing power closer to your production equipment, reducing latency and improving response times. Smart gateways and edge controllers process data locally, making split-second decisions without relying on cloud connectivity.
This distributed architecture proves particularly valuable for the following:
real-time quality inspection systems
predictive maintenance algorithms
autonomous machine coordination
local data aggregation and filtering
The result is faster response times and improved system reliability even when network connectivity fluctuates.
Artificial Intelligence at the Network Level
AI integration within automation networks enables self-optimizing systems that learn from production patterns. Machine learning algorithms analyze network traffic, predict potential failures, and automatically adjust communication parameters to maintain optimal performance.
These intelligent networks identify bottlenecks before they impact production, route critical messages through alternate paths during congestion, and adapt to changing operational requirements without human intervention.
Security Challenges and Solutions
Even though the future of industrial automation networks is bright, cybersecurity concerns must shape network architecture decisions in industrial environments. The convergence of OT and IT networks creates new attack vectors that don’t exist in isolated systems.
Network segmentation remains the cornerstone of industrial cybersecurity strategy. Properly implemented network zones create defensive barriers that contain potential threats while maintaining necessary connectivity between systems.
Zero Trust Architecture Implementation
Zero trust principles are gaining traction in industrial settings, requiring authentication and authorization for every network connection. This approach assumes no inherent trust, even for devices within your network perimeter.
Implementation typically involves these features:
multi-factor authentication for all network access
continuous device monitoring and behavior analysis
encrypted communication channels
regular access privilege reviews and updates
These measures significantly reduce your exposure to both external threats and insider risks.
Cloud Integration and Hybrid Architectures
Cloud connectivity transforms how you manage and optimize your manufacturing operations. Hybrid architectures combine local control with cloud-based analytics, providing the best of both worlds for industrial applications.
Local controllers maintain real-time operation while cloud services handle data analytics, machine learning model training, and remote monitoring capabilities. This separation ensures production continuity even during internet outages while enabling advanced optimization features.
Data Management Considerations
The volume of data generated by connected manufacturing equipment creates both opportunities and challenges. Effective data management strategies balance local storage requirements with cloud analytics capabilities.
Edge preprocessing reduces bandwidth requirements by filtering and aggregating data before transmission. Additionally, intelligent data routing ensures critical information reaches decision-makers while non-essential data gets stored for future analysis.
Preparing Your Facility for Network Evolution
Upgrading your automation network infrastructure requires careful planning and phased implementation. Start by conducting a comprehensive network assessment that identifies current capabilities, potential bottlenecks, and upgrade requirements.
Consider these key factors during your planning process:
bandwidth requirements for current and future applications
latency sensitivity of critical control systems
redundancy needs for high-availability operations
security requirements based on threat assessment
integration complexity with existing equipment
Phased deployment minimizes disruption while providing immediate benefits from upgraded network segments.
Staff Training and Development
Your team’s expertise directly impacts the success of network modernization efforts. Comprehensive training programs should cover both technical implementation and operational best practices.
Focus training efforts on network troubleshooting, security protocols, and system integration techniques. Additionally, develop internal expertise in emerging technologies like TSN and edge computing to reduce dependency on external support.
Taking Action on Network Modernization
The future of industrial automation networks is here, and early adopters gain significant competitive advantages. Start your network evolution journey by assessing your current infrastructure and identifying the most impactful upgrade opportunities.
And remember that partnering with experienced automation specialists accelerates your implementation timeline while reducing technical risks. These experts bring proven methodologies and industry best practices that transform complex network projects into strategic advantages.
That’s why you should partner with Metalcraft Automation Group. We believe your manufacturing operation deserves the reliability, performance, and capabilities that modern automation networks provide. Inquire about our diverse manufacturing automation solutions today and take the first step toward driving even more operational success.